I recently came across the PULL-framework in this article (Link) from Rob Snyder. It’s a smart way to better understand what creates necessary pull for a new product or service. Pull (Demand) is created by environmental conditions and is a necessary factor for the success of a new product or service. Regulatory changes, e.g. in data privacy, automatically create pull for products and services that solve specific challenges around the topic. Changes in the markt, e.g. an economic downturn, will naturally create pull for solutions that help customers cut costs and/or increase productivity.
Understanding pull can help us increase product success. It can guide us to focus on the right topics and problems, increase relevance with our potential customers and prevent us from building just another nice-to-have product.
What is the Pull-Framework?

The Pull-Framework described by Rob Snyder can roughly be divided into two-parts
- Defining the need: This covers the concrete project (P) someone has and why it is unavoidable (U) for someone.
- Understanding current choices: This covers understanding existing options (L) and solutions for the need and what they are lacking (L).
Both parts are interacting. What we are looking for is a strong and urgent need with a concrete market gap that is currently not covered. Only this combination creates the necessary pull for a new product or service.
An urgent projects doesn’t create necessary pull, if there are enough valuable and viable options out there. The same goes for unimportant projects that have no real dedicated solutions in the market (which explains why there are probably no real solutions available in the first place. Think about all the things people do in Excel.)
How can the PULL-Framework be extended?
To better understand pull for certain solutions I think it’s important to get a holistic view. This can be achieved by using concepts and other explanations to better understand the
- Enabling factors that clarify why the projects exists. Trends, economic or regulatory changes are only a few of the examples that can explain why an urgent project exists. It’s important to get a deep understanding of the enabling factors that together create the condition and need for a (new) solution.
- Constraining factors that explain why there are lacking options. Structural, economical or regulatory forces can prevent new solutions and clarify why current solutions are lacking certain important attributes. It’s important to be able to explain why the current solution space lacks options and describe how we overcome the constraints.
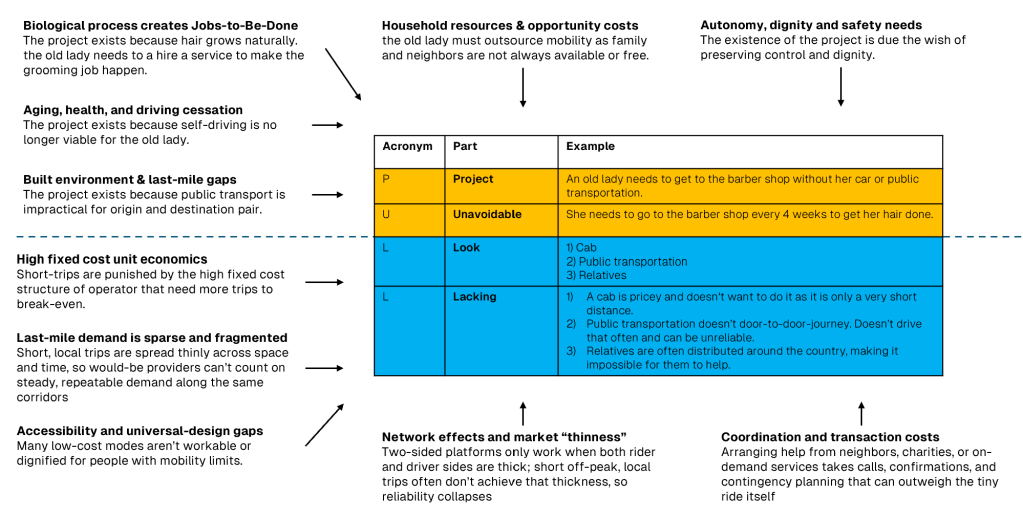
Example project: An old lady needs to go to the barber (without her car or public transportation.)
If we look at the enabling factors we can see that the project persists at the intersection of multiple concepts and phenomenon. The project entails a recurring JTBD, time-boxed urgency, reduced self-driving ability, last-mile transit gaps, resource and reliability constraints, autonomy and safety needs, and coordination frictions.
Together, these higher-order forces create strong pull for a solution that is short-distance-friendly, reliable to the minute, affordable at small scale, and supportive from door to door.
The constraining factors help us better understand why current solutions are not available. The cab market’s economics, rules, and incentives, systematically make very short trips both costly to buy and unattractive to sell.
Changes in lifestyle and economic developments lead to families being distributed all over the country. This makes relatives not an available option. High coordination and transaction costs, as well as lacking network effects and market thinness, must be taken into account when coming up with a potential solution.
Take away and further thoughts
By extending the PULL-Framework we can not only understand the Pull-Factor for a new product or service itself, but also the forces, trends and developments that shape it. It gives us a clearer picture into the enabling factors, which can helps us understand how resilient and important a customer project is.
By clarifying the constraining factors, we can better understand which forces maybe solveable by new developments, e.g. I think that current coordination and transaction costs for ride scheduling aimed at elderly people can be reduced significantly by A.I. solutions that take over phone operations.
Further improvements to better understand enabling and constraing factors can include
- Categorizing the forces, e.g. economical, regulatory etc.
- Assessing each factor’s strength, future development and therefore resilience.
- taking a development or topic, e.g. data privacy and define different projects that customers will most likely engage in